| |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
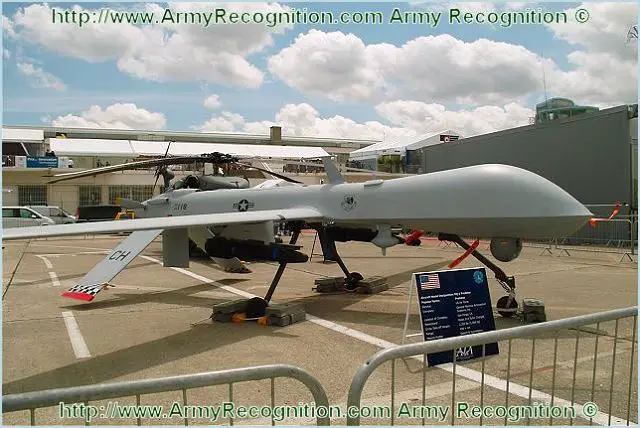
MQ-1
Predator Unmanned Aerial Vehicle UAV Drone |
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
||||||||||||||||||||||
The
MQ-1 Predator is a medium altitude, long endurance, unmanned aerial
vehicle system for use in risk areas minimizing to human life.The MQ-1
Predator is designed and manufactured by the American Company General
Atomics Aeronautical. Since 1995, Predator has logged over 405,000 flight
hours, of which over more than half have been during combat area deployments
to the Balkans, Southwest Asia, and the Middle East where Predator operates
in support of U.S. and NATO forces. Based upon the success of the program,
the U.S. Department of Defense transitioned the Predator program to
full rate production in August 1997, marking it as the first Advanced
Concept Technology Demonstration (ACTD) program to be designated an
Acquisition Category II Program. Predators are currently in production
for the U.S. and Italian Air Force. Land-based Predators have demonstrated
the ability to support maritime forces including carrier battle groups,
amphibious ready groups, and submarines. Predator is the only reconnaissance
system available in the U.S. inventory that can provide near real-time
video imagery day or night in all weather conditions via satellite worldwide
- without exposing pilots to combat fire. As the first successful unmanned
aircraft surveillance program, Predator provides tactical and strategic
intelligence to operational commanders worldwide. In July 1995, Air
Combat Command commissioned the 11th Reconnaissance Squadron, the U.S.
Air Force’s first operational Predator squadron. The second Predator
squadron, the 15th Reconnaissance, was commissioned in August 1997.
The third Predator squadron, the 17th Reconnaissance, was commissioned
in March 2002. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
-
Predator B: Predator B has the capacity to conduct multiple
missions simultaneously due to its large internal and external payload
capacity. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The
MQ-1 Predator has been configured with air-to-air or air-to-ground weapons
as well as a laser designator. THE MQ-1 Predator can carried precision
guided and smart munitions such as the Hellfire laser-guided anti-tank
missile and the BAT smart weapon. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
For
ease of operation and rapid deployment, each Predator UAV can be disassembled
into 6 main components and loaded in a container. This enables all system
components and support equipment to be rapidly deployed worldwide. A
5,000 by 125 feet (1,524 by 38 meters) runway is requested for UAVs
takeoff and land operations. The improved RQ-1B Predator UAV features
an ARC-210 radio, APX-100 IFF, ice mitigation system, upgraded engine,
and validated technical orders for operations and maintenance. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobility | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The
Predator, a growth evolution of the proven GNAT system, uses common
avionics and mechanical systems and incorporates a Rotax 4-cylinder
engine. The production version of the MQ-1 Predator aircraft is equipped
with a turbo-charged Rotax 914 engine producing 105 horsepower. This
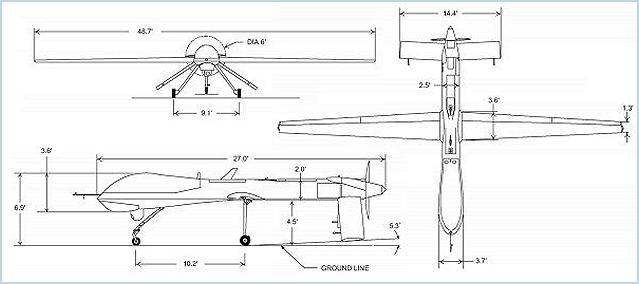
UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) measures 8 m long, 2,10 m high. The Predator
weighs 512 kg empty, and 1,043 kg Maximum Take Off Weight (MTOW). On
a typical mission the Predator cruises at an altitude of up to 7,620
m and 112 – 135 km/h, with maximum speed of 218 km/h. The MQ-1
Predator can maintain a 40 hours patrol over a large area, at a distance
of 645 km from its operating base. The payload capacity is 204 kg internal
plus 136 kg in external stores, and fuel capacity 300 kg. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accessories | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Configured
with a satellite data link system, Predator MQ-1 has an endurance of
40 hours and is equipped with an EO/IR stabilized gimbal containing
two color video cameras and a forward-looking infrared (FLIR) camera
as well as a synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Previously, Predators were
equipped with a synthetic aperture radar for looking through smoke,
clouds or haze, but lack of use validated its removal to reduce weight.
The cameras produce full motion video and the synthetic aperture radar
produced still frame radar images. There is sufficient bandwidth on
the datalink for two video sources to be used at one time, but only
one video source from the sensor ball can be used at any time due to
design limitations. Either the daylight variable aperture or the infrared
electro-optical sensor may be operated simultaneously with the synthetic
aperture radar, if equipped. All later Predators are equipped with a
laser designator that allows the pilot to identify targets for other
aircraft and even provide the laser-guidance for manned aircraft. This
laser is also the designator for the AGM-114 Hellfire that are carried
on the MQ-1. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combat Use | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
||||||||||||||||||||||
MQ-1 Predator UAV Drone Unmanned Aerial Vehicle technical data sheet specifications intelligence description information identification pictures photos images video United States American US USAF Air Force defence industry military technology
- Posted On



































